Base isolation is an important strategy for protecting structures from earthquake excitations. Base isolation attempts to isolate a structure from the external ground excitations. This has prompted great interest in the viability of base isolation for seismic protection of Civil structure. It is meant to protection enable building or non-building structure to survive in earthquake impact through a proper initial design or subsequent modifications
This
simulator considers multiple cases:
The user can vary the properties of the
structure, the isolation system and the earthquake motion, allowing for insight
into the influence of various parameters on the responses of the system.
Animation of the user designed systems facilitates visualization of parameter
effects. The base isolation simulation is intended to be used to increase
understanding and provide a conceptual "feel" for various parameter
changes on the performance of base isolated systems.
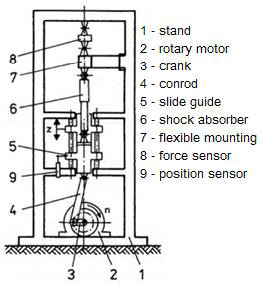
This Simulator offers how to operate and use the Shaking Table for Base Isolation Simulation, a picture of which is shown
below.
Research & Development Solution:
Shake Table – With the continual introduction of international building codes and regulations the importance of seismic resistant design is becoming increasingly important for most building structures. The shake table presents more advanced analysis with the introduction of dynamics of particular interest and value for structural dynamics research efforts and earthquake loss reduction.
Description:
A high-powered system for advanced research and curriculum the Table features:
- A maximum acceleration of 1.5g at full load.
- Maximum load of 120kg
- Maximum Velocity of 600 mm/sec
- High precision low friction linear bearings
- Linear motor no hydraulics or cams:
allows for greater precision of position and table displacement - Optional structure model:4 stories of nuclear plant dom constructions.
- Base Isolation Bearing
- Cost effective
Application:
Custom built for a research application the Table is generally available for a fraction of the cost of other high-powered systems in a similar class.